What Is Progesterone and What Does It Do?
Contents
- What does progesterone do once it is synthesized from pregnenolone?
- Mechanism of Progesterone Production
- Progesterone Levels for Men and Women
- What is progesterone going to cause if its levels are abnormal?
- Functions of Progesterone for the Female Body
- What is progesterone going to do during pregnancy?
- Role of Progesterone for the Male Body
- What is progesterone going to do for men besides support testosterone production?
- Progesterone and the Brain
- What is progesterone going to do for brain injury?
- Progesterone Deficiency: Signs and Symptoms
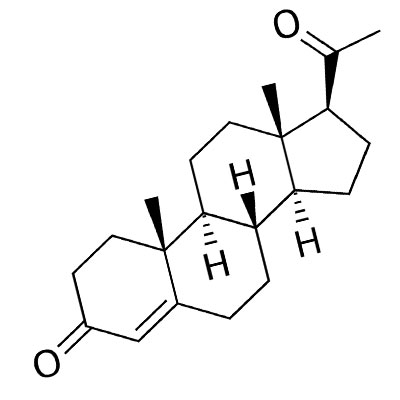
Trusted sourceProgesterone and ProgestinsHormone Health NetworkGo to sourceProgesterone is a hormone belonging to the progestogen group of steroid hormones. It is the precursor hormone for cortisol, aldosterone, estrogen, and testosterone. What is progesterone going to do for the adult body? Progesterone has numerous physiological and cognitive functions.
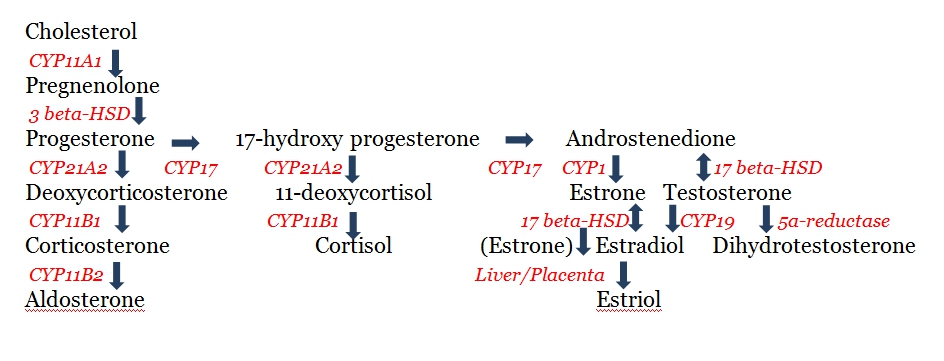
In the brain, progesterone takes on the role of a neurosteroid and has clinical applications for the treatment of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and epilepsy. As you can see in the chart in the next section, progesterone can go in one of two directions, converting into either Trusted source11-DeoxycorticosteroneScience DirectGo to sourcedeoxycorticosterone or 17-hydroxy progesterone.
It is in that second category that progesterone’s influence boosts either cortisol or testosterone and estradiol production. This is critical to understand because cortisol and testosterone are antagonistic of one another. In much the same way that cortisol inhibits growth hormone production when cortisol levels are high, testosterone secretion will decline. People with high stress levels often suffer from testosterone and growth hormone deficiencies.
What does progesterone do once it is synthesized from pregnenolone?
Aside from conversion into the other hormones shown, progesterone carries its own unique functions, as we will examine.
Mechanism of Progesterone Production
The mechanism of progesterone production begins with Trusted sourceWhat is cholesterol?Medline PlusGo to sourcecholesterol which is synthesized by the side-chain cleavage enzyme desmolase (CYP11A1) into pregnenolone. Next, the enzyme 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase converts pregnenolone into progesterone. As you can see, the process does not stop there. Through a series of further enzymatic conversions, progesterone becomes aldosterone, cortisol, testosterone, estradiol, and other critical hormones that the body needs every day. Estradiol is the most common form of estrogen in both males and females.
The body gets the cholesterol it needs to synthesize progesterone and other hormones in one of three ways:
- Uptake of LDL low-density lipoprotein
- Cholesterol that is synthesized from acetate within cells
- Cholesterol ester stored in intracellular lipid droplets
If you do not take in enough dietary cholesterol, your body will not have the necessary cholesterol for hormone production.
Progesterone Levels for Men and Women
Maintaining ideal progesterone levels is critical for women and men. Progesterone deficiency can be indicative of infertility as it influences testosterone and estrogen production.
The progesterone levels chart below shows the normal ranges of progesterone for women and men according to LabCorp. Oral contraceptive use can alter progesterone levels.
| Progesterone Levels Chart (ng/mL) | |
| Women: follicular phase of menstrual cycle | 0.1 – 0.9 |
| Women: luteal phase of menstrual cycle | 1.8 – 23.9 |
| Women: ovulatory phase of menstrual cycle | 0.1 – 12.0 |
| Women: pregnant, first trimester | 11.0 – 44.3 |
| Women: pregnant, second trimester | 25.4 – 83.3 |
| Women: pregnant, third trimester | 58.7 – 214.0 |
| Women: postmenopausal | 0.0 – 0.1 |
| Men | 0.0 – 0.5 |
What is progesterone going to cause if its levels are abnormal?
Aside from leading to deficiencies in other hormones, low progesterone levels may cause low sex drive, decreased red blood cell production, reduced bone density, impaired sleep, and many other issues both health and emotional-related.
Functions of Progesterone for the Female Body
In this section, we will look at progesterone functions that are solely for females. The following section about progesterone and the male body will cover additional progesterone benefits for men and women. Progesterone plays a crucial role in a woman’s regular monthly menstrual cycle. One function of progesterone is to prepare the endometrium (uterine lining) for embryonic implantation. Long before this, however, progesterone helps stimulate breast development during puberty.
Other pre-pregnancy benefits of progesterone include:
- Reducing estrogen production to prepare the uterus for pregnancy
- Decreasing breast cancer risk by lowering estrogen levels
- Normalizing blood flow during the menstrual cycle
What is progesterone going to do during pregnancy?
Benefits of progesterone for pregnant women include:
- Preparing the uterus for implantation following ovulation
- Nurturing the fetus in the first few months of pregnancy
- Decreasing feelings of nausea during the first trimester
- Reducing the risk of preeclampsia
- Preventing preterm labor
- Inducing the production of milk
- Reversing postpartum depression
- Maintain a supportive environment for the developing fetus
- more
During and after menopause, progesterone provides the following benefits:
- Reversing night sweats and hot flashes
- Decreasing weight gain
- Supporting vaginal lubrication
- Reducing feelings of depression
- Balancing emotional well-being
- bones
- Enhancing brain functions
- Improving sexual desire and performance
Role of Progesterone for the Male Body
Male production of progesterone occurs in the adrenal glands, the testes, and, in lesser amounts the brain. The importance of progesterone for men should never be overlooked, even though its levels are considered relatively low when normal. Without progesterone, a man will likely experience testosterone deficiency.
What is progesterone going to do for men besides support testosterone production?
Progesterone provides the following benefits for the male body (as well as for women):
- Balancing blood sugar levels
- Supporting sleep
- Improving heart health by stimulating vascular relaxation
- fat build-up in the blood through lipid profile support
- Normalizing blood clotting
- Acting as a natural diuretic
- Promoting the building of new bone cells
- thyroid hormone actions
- Supporting proper cellular oxygen levels
- Aiding pancreatic function and insulin release
- Reducing anxiety
- Improving metabolism
- Promoting thermogenesis for weight loss
- Normalizing zinc and copper levels
- Progesterone receptors in the skin help maintain elasticity, thickness, and firmness
Due to lower testosterone deficiency, men with low progesterone are at an increased risk of prostate cancer, osteoporosis, prostate enlargement, and arthritis.
Progesterone and the Brain
One aspect of progesterone function is its role as a neurosteroid hormone. Neurosteroids help regulate the transmissions of synapses or signals from one neuron to another. That is why progesterone is being closely looked at for its role in traumatic brain injury recovery. Progesterone exerts a protective influence on damaged brain cells and tissue.
What is progesterone going to do for brain injury?
One aspect of the protective effects of progesterone is that of reducing inflammation. Progesterone also prevents apoptosis (cellular death) in neurons. By preventing the premature death of brain cells, and stimulating neuroregeneration, progesterone helps repair the injured site.
Progesterone also supports serotonin receptor function in the brain to enhance serotonin activity. Adults with low progesterone levels may have a higher risk of addictions due to poor serotonin responses.
Progesterone Deficiency: Signs and Symptoms
The signs of progesterone deficiency are gender specific. While many symptoms of low progesterone are the same for men and women, there are some that only affect females or males.
The warning signs of low progesterone can also be mistaken for other hormonal imbalances. That is why blood analysis is critical to ensure the proper treatment.
Here is a chart of symptoms of progesterone deficiency:
Benefits of Progesterone Replacement Therapy for WomenThe benefits of using supplemental progesterone for women include:
- Lowering the risk of breast cancer due to elevated estrogen
- the risk of endometrial cancer
- Strengthening the bones to lower the incidence of osteoporosis
- Improving sleep
- Enhancing libido and sexual performance
- Supporting a healthy pregnancy
- Acting as a natural diuretic
- Increasing production of other essential hormones
- Improving PMS and menopausal symptoms
- Reducing feelings of depression and anxiety
- action of thyroid hormones
- blood sugar levels
- Normalizing blood clotting
- Supporting blood cell production
- Preventing cyclical headaches
- Promoting metabolism and weight loss
- Improving oxygen levels in cells
Doctor-prescribed progesterone replacement therapy offers women a wide range of benefits.Types of Progesterone Replacement Therapy for WomenWhen looking at the various types of progesterone replacement therapy, it is essential to remember that progesterone is not the same as progestin – a synthetic hormone. Progestin use has been linked to increased risk of breast cancer, blood clots, and heart attacks in some menopausal women. Natural progesterone does not carry that same risk.Women with a progesterone deficiency may require treatment for the following reasons:
- To start menstruation
- For supplementation when ovaries do not produce enough progesterone
- To counteract medications that lower progesterone
- For birth control (synthetic progestin)
- For replacement following oophorectomy (surgical removal of ovaries)
- During menopause
The following treatments may be prescribed to women:
- Vaginal suppositories – typically inserted two to three times per day
- Vaginal gel – administered once daily
- Oral capsules – inserted vaginally up to three times a day (unapproved by the FDA for vaginal use)
- Vaginal inserts – administered up to three times a day
- Progesterone shots – injected into the buttocks once a day
- Progesterone cream – applied to the skin once or twice a day
- Skin patch – applied daily
Benefits and Types of Progesterone Therapy for MenThe benefits of progesterone therapy for men include:
- Balancing critical hormone levels
- Supporting proper heart and brain functions
- Reducing body sweat and odor
- Improving prostate functions and urinary flow
- Enhancing sexual performance and desire
- Strengthening bones
- Supporting mood, sleep, metabolism, and energy
For men wondering how to increase progesterone levels, the hormone specialist will likely prescribe a compounded cream. The cream provides a customized amount of progesterone delivered through the skin into the bloodstream.What Happens If You Have Too Much Progesterone?Although not as common, having too much progesterone is also problematic. Elevated progesterone is associated with a condition called congenital adrenal hyperplasia – although it is a symptom, not a cause. High progesterone levels can also increase the risk of breast cancer.Since elevated progesterone levels can lead to increased estrogen in men by way of testosterone production, concerns may include:
- Weight gain
- Depression
- Fatigue
- Enlarged prostate
- Erectile dysfunction
Importance of Keeping Progesterone Levels in BalanceWe cannot stress enough the importance of maintaining balanced progesterone levels. Maintaining progesterone balance is critical for the many other hormones it influences.Progesterone benefits the body, mind, and emotions. It is more than just a pregnancy hormone. If you have concerns about low progesterone levels, please contact our hormone clinic. Medical advisors are available for free, confidential consultations by phone. Balanced hormone levels impact all areas of your life. We can help.
| Symptoms 0f Progesterone Deficiency | Males | Females |
| Depression, anxiety, stress, mood changes, irritability | X | X |
| Decreased sex drive | X | X |
| Hot flashes, night sweats | X | X |
| Weight gain | X | X |
| Cyclical headaches | X | |
| Infertility | X | X |
| Andropause symptoms | X | |
| Menopause symptoms | X | |
| PMS | X | |
| Menstrual irregularities, heavy bleeding | X | |
| Endometriosis | X | |
| Swollen, tender, painful breasts | X | X |
| Polycystic ovarian syndrome | X | |
| Postpartum depression | X | |
| Miscarriage | X | |
| Swollen ankles | X | |
| Vaginal dryness | X | |
| Fibroids | X | |
| Enlarged prostate | X | |
| Prostate cancer | X | |
| Low energy, fatigue | X | X |
| Insomnia, sleep issues | X | X |
| Imbalanced blood sugar levels | X | X |
| Urinary flow changes | X | X |
| Body sweat or odor changes | X | |
| Reduced bone density | X | X |
| Erectile dysfunction | X | |
| Thinning or balding of hair | X | X |
| Increased body hair | X | X |
| Decreased muscle mass | X | X |
| Higher cancer risk | X | X |
| Impaired memory or cognitive functions | X | X |
| Thinning skin | X | X |
| Higher risk of heart and arterial disease | X | X |
| Anemia (caused by low testosterone) | X | X |
- Nathalie Goletiani, MD, Diana R Keith, PhD, Sara J Gorsky
- Lorraine Dennerstein, AO, MBBS, PhD, DPM, FRANZCP, Dr. Spencer C Gardner, Gordon Gotts, J B Brown, Michael Smith, PhD, Dr. Graham Burrows
- Santiago Palacios, MD, PhD, Dr. Andrea Mejía
- Allan Lieberman, Luke Curtis
- P.-A. Regidor
Progesterone: Review of Safety for Clinical Studies
Progesterone and the premenstrual syndrome: A double blind crossover trial
Progestogen safety and tolerance in hormonal replacement therapy
In Defense of Progesterone: A Review of the Literature
Progesterone in Peri– and Postmenopause: A Review