Contents
- How Does the Body Produce Estrogen?
- Where is estrogen produced?
- What is the estrogen production pathway?
- Function of Estrogen for the Female Body
- What does estrogen do for the female body?
- Function of Estrogen for the Male Body
- Why do men have estrogen and what does it do for them?
- What Happens When the Body Has Low Estrogen?
- What Happens When the Body Has Too Much Estrogen?
- How to Know If You Need Estrogen Therapy
- How to Reduce Estrogen Levels

Perhaps one of the most important reasons the body requires estrogen is that it helps to regulate the liver’s production of cholesterol – the precursor building block of estrogen and other steroid hormones.
Estrogen is a steroid hormone primarily associated with female sexual development but also essential for the following functions in men and women:
- Preservation of bone mineral density
- Support for cognitive functions and memory – neuroprotective
- Maintenance of the endothelium (arterial wall lining)
- healthy lung functions
- Protection of skin texture and elasticity
There is a need to keep the body’s estrogen levels in proper balance to protect these functions.
Three types of estrogen occur naturally, with a fourth only present during pregnancy. The steroid hormones that make up the oestrogen classification include:
- Estradiol
- Estrone
- Estriol
- Estetrol
Men and women need estrogen for their bones, hormones, brain functions,
and heart health.
How Does the Body Produce Estrogen?
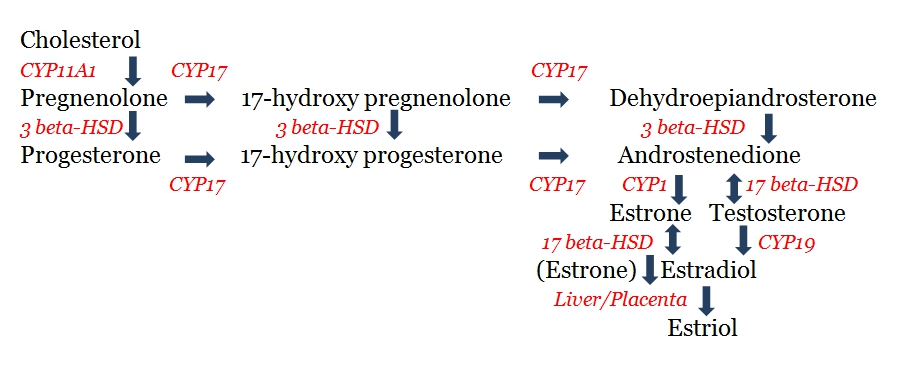
Estrogen production is similar to that of other steroid hormones and follows a specific pathway. The process starts with the enzymatice synthesis of cholesterol which, in turn, becomes pregnenolone. The body will use a cholesterol precursor coming from one of the following methods:
- Synthesized fromr acetate within the cells
- Ester stores of cholesterol inside intracellular droplets of fat (lipids)
- Uptake of LDL cholesterol
Where is estrogen produced?
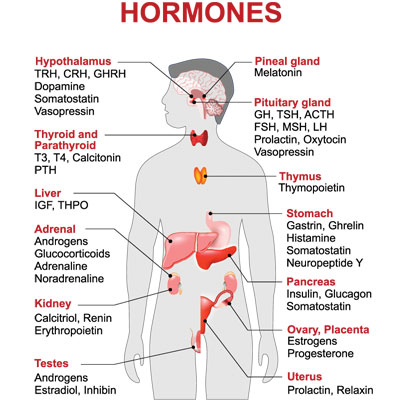
Steroidogenesis of estrogen occurs primarily in the gonads, with a portion coming from the adrenal glands and other tissues (breasts, brain, fat, liver). For males, that means the testes, and for females, the ovaries.
What is the estrogen production pathway?
After cholesterol is processed into pregnenolone, estrogen production can occur via conversion into progesterone or 17-hydroxy pregnenolone.
If the conversion to 17-hydroxy pregnenolone occurs, the next step is either:
- Synthesis to dehydroepiandrosterone > androstenedione > estrone > estradiol > estriol
- Or dehydroepiandrosterone > androstenedione > testosterone > estradiol > estriol
If the conversion to progesterone occurs, the next step is synthesis to 17-hydroxy progesterone, followed by androstenedione, and then either estrone or testosterone followed by estradiol and estriol.
Function of Estrogen for the Female Body
Primary estrogen function in women begins in the ovarian follicles where estradiol production occurs. Estradiol is the main estrogen in a female’s body from the time she starts having a period until menopause. The levels of estradiol in the bloodstream fluctuate according to various times of the menstrual cycle. The amount of estrogen is highest in the middle of the menstrual cycle and lowest during menstruation.
A small amount of estradiol comes from estrone produced in fat cells, adipose tissue, and muscle via aromatization of testosterone. Estrone is a woman’s second greatest source of estrogen behind estradiol during childbearing years. However, after menopause, the body only produces estrone. Estriol is present in a very limited quantity until pregnancy when it increases. Finally, estetrol is the least form of estrogen, synthesized by the fetal liver from estradiol and estriol during pregnancy.
What does estrogen do for the female body?
One of the primary roles of estrogen is to prepare the uterus for pregnancy by building up the endometrial lining. If fertilization does not occur, estrogen levels rapidly decrease, and menstruation commences. If pregnancy occurs, estrogen and progesterone work together to prevent ovulation.
The function of estrogen also depends on the type of estrogen:
Estradiol – the primary estrogen source, provides the following benefits:
- Breast development and widening of the hips – during puberty
- Boosting cortisol production
- Decreasing bone resorption rates to improve bone mineral density and prevent bone loss
- Maintaining healthy vaginal lining and lubrication
- Promoting proper lung functions
- Supporting skin elasticity and thickness
Estrone – the second source of estrogen has a slightly weaker activity level than estradiol and has the following positive benefits:
- Promoting production of nitric oxide to help blood flow
- Protecting the endothelial lining of blood vessels
- Supporting heart and brain functions
- Provides neuroprotective benefits for the brain following an injury
Estriol – when not pregnant, a woman will have very low estriol levels. The placenta produces estriol during pregnancy, and it helps promote fetal growth and development, as well as lactation preparation. Estriol exits the bloodstream rapidly and may help inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer cells induced by estradiol.
Estetrol – its role during pregnancy is not well-defined. Estetrol may impact liver function, lipid metabolism, and bones.
Estrogen functions in women support brain and heart health, bones, skin, vaginal health, and uterine lining for pregnancy.
Function of Estrogen for the Male Body
The majority of estrogen in males comes from the Leydig and Sertoli cells in the testes, with additional supply coming from the adrenal glands and other tissues. The more belly fat a man has, the higher his estrogen levels are likely to be. Belly fat produces the enzyme aromatase that converts free testosterone in the bloodstream to estradiol.
Why do men have estrogen and what does it do for them?
Estrogen is a vital steroid hormone that helps to keep testosterone levels in balance. If there is too much testosterone in the bloodstream, aromatase will convert some of it into estradiol. Estrogen plays a critical role in maintaining the lining of arterial walls to support circulation and heart health. Estradiol plays an essential role in erectile function, libido, and spermatogenesis. A male has estrogen receptors in the corpus cavernosum of the penis, as well as in the testes and brain. Men need properly balanced testosterone and estrogen levels for a healthy libido. Estrogen acts on the brain to influence erectile functions, and too much can inhibit testosterone production vital to a firm erection.
An important function of estrogen in men is to work with calcium, vitamin D, and other hormones to prevent bone loss. If the body does not have enough estrogen to slow bone resorption, then old bone cells are lost faster than new ones are formed. Males with low estrogen levels have a three-fold risk of hip fractures due to osteoporosis.
What is estrogen going to do to a man who has too much or too little of it in his body?
Elevated estrogen levels in older men can increase the incidence of death from chronic heart failure by 133%. Too little estrogen also has the same issue, only worse – the risk factor increases to 317%.
Men with low estrogen levels have a higher incidence of all-cause mortality and suffer more deaths than those with estrogen in the optimal range.
Estrogen is crucial for a man’s bones and heart health. Too much or too little estrogen can increase the risk of early death.
What Happens When the Body Has Low Estrogen?
Estrogen deficiency can occur if its precursor hormones are also low. Surgical removal of a woman’s ovaries causes an immediate and significant decline in estrogen levels. Male or female, a lack of estrogen can have dire consequences for the body.
What is estrogen going to do to the body if its levels are too low?
Here are some low estrogen symptoms everyone should know:
- Depression and mood changes
- Thinning or drying of the skin
- Vaginal dryness – females
- Lack of sexual desire
- Insomnia or other sleep disturbances
- Brittle and weak bones
- Night sweats
- Hot flashes
- Weight gain – belly fat
Estrogen deficiency can cause weight gain, depression, low libido, brittle bones, insomnia, hot flashes, and other symptoms.
What Happens When the Body Has Too Much Estrogen?
Monitoring estrogen levels is crucial, especially in later years. High estrogen in women after menopause could increase the risk of cancer.
What is estrogen going to do if a woman produces more than her body needs?
Symptoms of too much estrogen in women include:
- Darkening of the skin
- Abdominal weight gain
- Increased risk of coronary artery disease
- Uterine fibroids
- Low sex drive
- Fatigue
- Fibrocystic breasts
- Menstrual problems – heavy, light or irregular bleeding
- Depression, mood changes, increased anxiety
Other issues for males with too much estrogen include:
- Infertility
- Erectile dysfunction
- Gynecomastia – breast enlargement
Too much estrogen can lead to weight gain, increased risk of strokes, coronary artery disease, and more.
How to Know If You Need Estrogen Therapy
Estrogen replacement is often beneficial for women during menopause. However, it is essential to know if that is the best option. The only way to determine that is through comprehensive hormone blood testing to measure the various hormone levels that can decline at this stage of a female’s life.
Estrogen deficiency can lead to osteoporosis, heart disease, and many other health risks. The problem is that some doctors prescribe estrogen without checking progesterone and testosterone levels. During menopause, all three of these hormone levels decline. Unfortunately, women who have a higher degree of belly fat see more of a testosterone conversion into estradiol. When that occurs, testosterone levels further decrease, and estrogen rises. The result is a condition called “estrogen dominance” that increases fat retention. Gaining more weight means more aromatase and further testosterone decline.
What is estrogen therapy going to consist of and is there more than one type of treatment?
Depending on the symptoms of estrogen deficiency, the doctor may prescribe pills, patches, skin gel, vaginal cream or rings, or a nasal spray. If the only issues a woman has is vaginal wall thinning and dryness, then the doctor will likely offer a vaginal preparation. A benefit of that is a reduced risk of side effects.
Hormone specialists often prefer to avoid oral pills as they must go through the liver and can impact the production of other hormones.
If a woman has her uterus intact, she should also use progesterone with estrogen to protect against endometrial cancer. Progesterone is not the same thing as synthetic progestin – the medication that increased dangerous risks in the Women’s Health Initiative study. Natural, bioidentical progesterone is safe to use.
Estrogen therapy by itself is beneficial for the treatment of menopausal symptoms in women who no longer have a uterus. Men can also use it to treat very low estrogen levels, but this is rare.
Blood analysis of multiple hormone levels is crucial before starting any type of hormone replacement therapy.
How to Reduce Estrogen Levels
Estrogen dominance is just as serious for men as it is for women. If there is too much estrogen in the bloodstream, it is essential to understand how to lower estrogen levels. There is a delicate balance of testosterone/estrogen/progesterone that must be maintained for optimal health.
An estrogen blocker is the treatment of choice when you need to prevent or inhibit testosterone conversion to estrogen.
What is an estrogen blocker?
A medication called anastrozole blocks the action of the enzyme aromatase on testosterone. The result is increased free testosterone left in the bloodstream and lower estrogen levels.
Why Balanced Estrogen Is Crucial for the Body
Maintaining natural estrogen levels in their ideal range is vital for a healthy body. Estrogen protects the bones, brain, heart, blood vessels, and more.
Whether you need to know how to increase estrogen or decrease it for hormonal balance, we can help. Our hormone clinic works with men and women over age thirty throughout the US. We offer free consultations by phone with an experienced medical advisor who can guide you through the steps of determining hormone levels.
If you have further questions about what is estrogen and how much is in your body, please contact us today.
- Garnet Anderson, Ph.D.
- Ross Prentice, Ph.D.
- Rogerio A. Lobo
- Dr. Wilfredo Lopez-Ojeda, PhD, MS
- Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT; Kimberly Holland
- Cleveland Clinic
- Risks and Benefits of Estrogen Plus Progestin in Healthy Postmenopausal Women
Garnet Anderson, Ph.D. Senior Vice President and Director Public Health Sciences Division, Fred Hutch. Study: Estrogen
Dr. Prentice is a biostatistician who specializes in chronic disease prevention. He develops methods used in the design and analysis of clinical and population studies, with an emphasis on dietary and hormonal changes that may reduce the risk of major cancers and cardiovascular diseases.
Dr. Rogerio A Lobo, MD is a doctor primarily located in New York, NY, with another office in New York, NY. He has 46 years of experience. His specialties include Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism, Gynecology, Obstetrics & Gynecology, Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility.
A thought-provoking scientist, innovator and aspiring senior medical/scientific writer. Author, editor and member of reputable journals in the fields of medicine and basic sciences. An avid medical educator and practitioner of the art of integration among basic, clinical sciences and technology for medical curricula. Trained as a classical clinical anatomist and neuroscientist (PhD) with over 25 years of experience including MedEd and health sciences instruction. Experienced gross anatomist (cadaveric), skilled dissector, histologist and physiologist.
The Heart and Estrogen/Progestin Replacement Study Revisited
Estrogen & Hormones Reviewed By: Dr. Leslie Cho.
Study Source