Contents
- What Is Oxytocin Hormone
- What kind of hormone is oxytocin?
- How is oxytocin a peptide hormone?
- Is oxytocin a hormone or neurotransmitter?
- How is oxytocin a stress hormone, and how does it have any influence on a person’s emotional state?
- How Is Oxytocin Regulated?
- What Happens When Oxytocin Hormone Is Low
- What Happens When Oxytocin Hormone Is High
- How Do You Check Oxytocin Hormone
- How Do You Balance Oxytocin Hormone
The Trusted sourceWhat is Oxytocin?Hormone Health NetworkGo to sourceoxytocin hormone definition is two-part – one that it helps women during childbirth as being responsible for signaling the womb’s contractions during labor, and the other of helping with male reproduction.
However, that is not the only way to describe this hormone. Oxytocin definition is also called the “cuddle” or love hormone as its levels are higher in coupled in the early stages of their romance. People with Trusted sourceOxytocin in human plasmaNCBIGo to sourcenormal levels of oxytocin tend to have better social interactions, are more open and trusting, and exhibit extrovert rather than introvert tendencies.
In this report, we will look at the following:
- What does oxytocin hormone do
- How oxytocin is produced
- What happens when oxytocin hormone levels are low
- What can occur if you have high oxytocin levels
- How to check oxytocin hormone levels
- Steps to take to balance oxytocin
Oxytocin, also called the love hormone, has multiple functions for men and women.
What Is Oxytocin Hormone
Oxytocin is a chemical released into the bloodstream as well as a medication used to help stimulate childbirth.
What kind of hormone is oxytocin?
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone as well as a neuropeptide. Peptide hormones are long amino acid chains that can act systemically rather than only on individual cells. Neuropeptides are small protein-like molecules that neurons use for communication with one another. The difference between peptides and neuropeptides is in the cell types associated with them. Peptide secretion occurs from neuroendocrine cells and neuropeptides from neuronal and some glial cells. The peptides travel through the bloodstream to distant tissues whereas neuropeptides release their signals on neighboring cells.
How is oxytocin a peptide hormone?
Oxytocin is a peptide consisting of nine amino acids. One IU (international unit) of oxytocin equals 2 micrograms of pure peptide. Its sequence is as follows:
Cysteine – tyrosine – isoleucine – glutamine – asparagine – cysteine – proline – leucine – glycine (CYIQNCPLG)
What type of hormone is oxytocin when it is acting as a neuropeptide?
When oxytocin acts as a pituitary neuropeptide, it influences social and emotional behaviors.
What is oxytocin hormone going to do for females and males?
Females
- Signaling labor contractions by the uterine muscles
- Increases prostaglandin production that furthers labor
- Stimulates lactation following birth by moving milk into the breasts
- Causes milk release in response to suckling response
Males
- Helps influence testosterone production
- Assists with sperm movement
If oxytocin assists with testosterone and sperm, is oxytocin a steroid hormone?
While oxytocin itself is not a steroid hormone, its expressing neurons contain enzymes that assist with steroid metabolism.
Is oxytocin a hormone or neurotransmitter?
Oxytocin is both a hormone and a neurotransmitter. The role of oxytocin as a neurotransmitter occurs when its release takes place in the brain. There, it can impact cognitive, emotional, and social behaviors. Oxytocin has been described as part of a complex neurochemical system that helps the body adapt to highly emotive situations.
How is oxytocin a stress hormone, and how does it have any influence on a person’s emotional state?
There is much to understand about how oxytocin affects the body and the brain. Aside from the fact that oxytocin influences the bond between a mother and baby, it may play many other roles. Here are some other names associated with oxytocin: trust hormone, the sexual arousal hormone, as well as expressing an action in addiction, stress, anxiety, empathy, relationship-building, and recognition.
It is also through this mechanism that earned oxytocin the love hormone nickname. Its influence on social behavior, mother-baby bonding, and sexual arousal are why some people call it the “cuddle chemical.”
As a medicine, doctors may give oxytocin to women to speed up and strengthen labor contractions or to assist with the placenta delivery and reduce heavy bleeding risk by contracting the uterus.
Oxytocin is a hormone that influences many activities in the human body and brain.
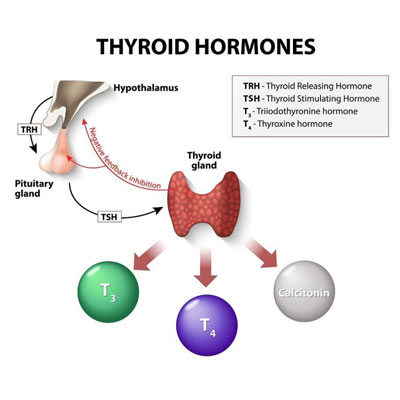
How Is Oxytocin Regulated?
Oxytocin hormone production occurs in the magnocellular neurosecretory cells of the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei in the hypothalamus before it is secreted into the bloodstream by the posterior pituitary gland. After production, oxytocin travels from the hypothalamus to the Herring bodies at the axon terminals of the posterior part of the pituitary gland to await a triggering action. Neuronal electrical activity in the hypothalamus occurs when the cells are excited, which triggers the release of oxytocin into the bloodstream. Oxytocin release also occurs during sex; again, one of the reasons it is called the “love hormone.”
Non-neural sources of oxytocin outside the brain have been found in the following:
- The interstitial Leydig cells in males
- The corpus luteum and placenta in females
- Retina
- Pancreas
- Thymus
- Adrenal medulla
The production cycle for oxytocin occurs through a positive feedback mechanism based on a trigger effect. When the trigger occurs, oxytocin is released, which then stimulates the action. An excellent example of this is when the suckling of an infant triggers the letdown of the mother’s milk. Another example is when uterine contractions begin. With each contraction, more oxytocin is released into the bloodstream, which then further stimulates future contractions in frequency and intensity.
When oxytocin hormone function is associated with milk movement into the breast, its production ceases once the suckling motion of the infant stops.
Oxytocin hormone regulation is via a positive feedback mechanism that results in an action stimulating oxytocin release, which then furthers that action.
What Happens When Oxytocin Hormone Is Low
There is limited research on low oxytocin hormone levels. What does the hormone oxytocin do if its levels are lower than normal?
Women who have low oxytocin levels may have difficulty with milk letdown during breastfeeding.
Some research has linked low oxytocin hormone effects to depression. Low oxytocin peptide hormone levels have also been associated with autism and autistic spectrum disorders such as Asperger syndrome. More research into these areas is necessary to determine if medicinal oxytocin can help provide treatment.
Low levels of oxytocin may have numerous other effects on a person, including:
- Poor socialization – since oxytocin helps to foster social interaction and relationships, people with low levels may exhibit social anxiety or introversion tendencies.
- Low libido – because oxytocin release also occurs with sexual desire, it may be difficult to attain sexual arousal and orgasm. Sex can be seen as mechanical rather than emotional or spontaneous.
- Depression – people with low oxytocin hormone levels may be depressed, anxious, withdrawn, or fearful of others.
- Aggressive behaviors – just as low oxytocin can lead to depression, it can also cause feelings of anger and aggressive actions.
- Distrust – oxytocin is called the “trust hormone” for good reasons – it helps with communications and social interactions. Feelings of distrust in others may be due to low oxytocin levels.
- Poor communication – individuals with low oxytocin levels may exhibit negative behaviors and communication skills with others.
- Sugar cravings – low oxytocin levels can cause the body to seek out sugar, resulting in a sugar-craving cycle that can lead to overconsumption of sweets.
Low levels of oxytocin are often associated with elevated cortisol levels. When cortisol production increases, oxytocin release declines.
Low oxytocin levels can slow labor, inhibit breastfeeding, and lead to many issues in daily life.
What Happens When Oxytocin Hormone Is High
High levels of oxytocin hormone in men are linked to a condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia. BPH leads to an enlarged prostate gland in more than half of men age 50 and over. When BPH occurs, it may make it difficult to pass urine.
Although not considered to be abnormally high, both females and males have been found to have higher oxytocin levels during the first six months of a new romantic relationship as compared to non-attached single adults. Hence, the chemical “love” reaction of oxytocin.
These types of bonds are not only seen with dating but also with being part of a social group or “tribe.” One’s tribe can consist of family, friends, co-workers, or even those who share a similar passion – such as having a favorite sports time.
That is where too much oxytocin can become a problem as it can lead to negative behaviors to “protect” one’s “tribe.” In some studies, participants who received oxytocin were more likely to lie. Elevated oxytocin levels can lead you to put up walls between people not part of your group or inner circle. Fear, mistrust, aggression, envy, prejudice, and xenophobia are all possible responses. Jealousy and suspicion can occur.
Elevated oxytocin hormone levels can lead to BPH in men and a host of emotional and social problems in adults.
How Do You Check Oxytocin Hormone
Is oxytocin a hormone that can be tested by a lab? As a neurotransmitter, it is difficult to test for hormone oxytocin levels in the brain. That leads to either blood, urine, or saliva testing as potential options for checking oxytocin levels.
Unfortunately, checking oxytocin hormone levels in this way is uncommon. The most likely assessment by a doctor for oxytocin imbalance is a symptom review as well as ruling out other potential health issues and hormone problems.
By contacting a hormone specialist, you can have your oxytocin, cortisol, and other hormone levels checked, if necessary.
A hormone specialist can help you determine if your oxytocin levels are in balance.
How Do You Balance Oxytocin Hormone
Doctors know how to increase oxytocin hormone during labor by delivering the medication Pitocin (synthetic oxytocin) into the bloodstream. An injection of Pitocin helps to start or strengthen contractions to move the labor along. Pitocin also reduces uterine bleeding after birth.
Side effects of Pitocin include rapid heartbeat and potential unusual bleeding. If too much oxytocin hormone therapy is administered too fast, it could result in a ruptured uterus.
It is important for everyone to have balanced oxytocin hormone levels as that improves social interaction and emotional well-being.
Here are some ways you can increase oxytocin levels naturally:
- Touch – hugging, hand-holding, massages, cuddling a pet, even shaking hands can help stimulate sensors in the hypothalamus that produce oxytocin
- Do something for someone else – giving a gift, volunteering, getting together with friends, even connecting with someone via phone or social media can help increase oxytocin levels
- Exercise – physical activity, especially yoga, can help boost oxytocin
- Relax – listen to music, meditate, or engage in enjoyable activities to reduce cortisol and increase oxytocin hormone levels
- Supplements – vitamin C, melatonin, probiotics, fenugreek, anise seed, and sage are potential oxytocin boosters
If you suspect low oxytocin levels, the best thing you can do is contact a hormone specialist before taking any action. HGH Doctor hormone clinic offers free, confidential consultations by phone to men and women throughout the US.
- Elizabeth A. Lawson, MD, MMSc
- Nadia Micali, MD, PhD, Marta Crous-Bou, Janet L Treasure,PhD, FRCP, FRCPsych, Elizabeth A. Lawson, MD, MMSc
- Mary R Lee, MD, Karl B Scheidweiler, PhD, Xingxing Diao, PhD, . Fatemeh Akhlaghi, Doctor of Pharmacy; PhD, Alex Cummins, Marilyn A Huestis, BS, MS, PhD, MD, Lorenzo Leggio, MD, PhD, Bruno Averbeck, PhD
- Navneet Magon and Sanjay Kalra
The effects of oxytocin on eating behaviour and metabolism in humans
Association Between Oxytocin Receptor Genotype, Maternal Care, and Eating Disorder Behaviours in a Community Sample of Women
Oxytocin by intranasal and intravenous routes reaches the cerebrospinal fluid in rhesus macaques: determination using a novel oxytocin assay
The orgasmic history of oxytocin: Love, lust, and labor